Self-Employment Tax Solution
Ways to Reduce the Informal Economy

The informal economy, also known as informality, remains a significant challenge worldwide. It deprives governments of vital revenue, perpetuates economic inequality, and hinders social protection coverage.
Informality is particularly prevalent in sectors like informal own-account work (self-employment) and digital labour platforms, where traditional regulatory frameworks struggle to keep pace with evolving work models.
However, digital transformation offers powerful tools to reduce informality by improving tax compliance, formalizing self-employed workers, and enabling effective taxation of digital labour platforms.
In this post, we will explore innovative digital solutions, including traceCORE Self-Employment Tax Solution and traceCORE Platform Employment Tax Solution that can drive down informality and create more inclusive, transparent economies.
What Is the Informal Economy?
The informal economy refers to all economic activities that take place outside the formal regulatory and tax frameworks of a country. These include everything from small-scale street vendors and home-based artisans to unregistered service providers and gig workers who operate without formal contracts or legal protections.
Informal economic activities have the following indications:
-
Lack of registration with government authorities.
-
Tax noncompliance.
-
No formal labor contracts and social protections.
-
They often escape legal oversight, such as labor laws, health and safety standards, and environmental regulations.
How Informality Affects Economies
While informality provides livelihoods for many, especially in developing countries, it also creates significant economic and social challenges:
Loss of Tax Revenue
Informal businesses and workers typically do not pay income or corporate taxes, which results in billions of dollars in lost government revenue globally.
Due to tax revenue loss, governments struggle to fund essential public services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
Lack of Fair Competition
Informal enterprises often avoid formalization and everything that comes with it — taxes, licenses, and compliance.
This creates unfair competition against formal businesses that follow rules, discouraging investment and growth in the formal sector.
Limited Worker Protection
Informally employed workers lack access to minimum wages, workplace safety, social security, and benefits, which results in poorer health, job insecurity, and lower productivity.
If informality levels are especially high in certain countries, it can reduce overall labor market efficiency and economic output.
Restricted Access to Financial Services
Informal businesses often can’t access bank loans, credit, or formal supply chains due to lack of registration and credit history.
Such restrictions limit their ability to grow, innovate, and create more jobs.
Slower Economic Growth
Large informal sectors are often associated with lower GDP growth.
Informality traps workers and businesses in a cycle of low income and vulnerability, while the economy loses potential multiplier effects from investment, innovation, and skill development.
Weaker Institutional Trust
Widespread informality can indicate weaker institutions and lack of enforcement capacity.
It may erode trust between citizens and government, making reforms and policy implementation more difficult.
How Much of the Informal Economy Is Made Up of Informal Employment?
Informal employment constitutes the vast majority of the informal economy. While exact percentages vary by region and source, informal employment accounts for around 70-90% of the informal economy’s total output in many developing countries, namely in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, according to traceCORE’s estimates.
Informal employment includes:
-
Own-account workers (self-employed without formal business registration).
-
Contributing family workers.
-
Wage workers in informal jobs without contracts or social protection.
In 2025, ILO also reported that informal employment accounted for 58% of the global workforce, which is equivalent to over 2 billion workers.
Targeting informal workers directly using cutting-edge digital tax solutions addresses the largest segment of informality and its associated challenges.
Focusing on formalizing informal employment through digital transformation solutions can significantly reduce the informal economy’s size.
If this is what you’re currently struggling with in your country, contact us today to learn how traceCORE can assist you, and what tools can be used to reach your goals.
Simplifying Formalization for Individual Workers Using Self-Employment Tax Solutions
Digital self-employment tax solutions are user-friendly online or mobile platforms that help self-employed workers register, report income, and pay taxes easily.
Such tools help more individuals transition to formal employment due to multiple reasons, here are three key ones:
Lower Barriers to Registration
Instead of complicated paperwork, workers can register and file taxes using simple apps or websites.
Automated Income Tracking
Digital tools often integrate with payment platforms to automatically track earnings, reducing errors and underreporting.
Transparent tax calculations
Apps can automatically calculate taxes based on income brackets, making compliance straightforward.
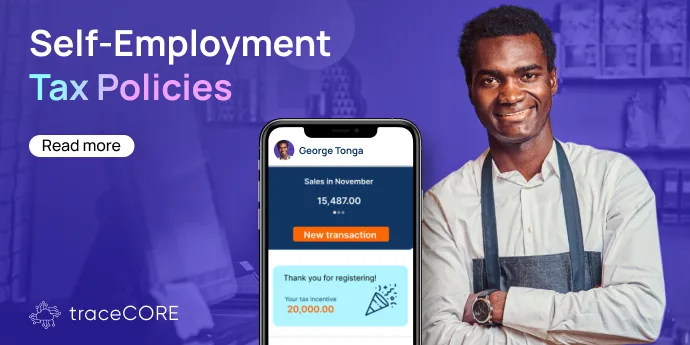
traceCORE Self-Employment Tax Solution is exactly a tool like that, providing individual workers with the access to government services, including online tax registration, automatic tax filing and electronic fiscal receipts, as well as ways to receive payments from customers and pay taxes.
With this solution, it’s very easy to register as self-employed using personal identification details and pay taxes from anywhere instead of having to schedule physical appointments.

After its implementation, countries can enable governments to widen the tax base with minimal administrative cost, increase tax compliance among the self-employed and informal entrepreneurs, and bring more workers into the social protection system, improving their access to healthcare and pensions.
To learn more about this system, click here.
Formalizing Gig and Platform Work with Digital Labour Platform Taxation
Digital labor platforms, such as Uber, Airbnb, or freelance marketplaces like Upwork, Fiverr and many others, facilitate gig work.
According to Business Research Insights, the gig economy market, valued at US $556.7 billion in 2024, is forecasted to increase to US $646.77 billion in 2025 and surpass US $2,146.87 billion by 2033.

Taxation on the gig platforms means collecting tax data directly from the platform based on workers’ earnings.
Here’s how such solutions help reduce informality:
Automatic Reporting
Platforms report worker incomes directly to tax authorities, reducing underreporting or tax evasion.
Improved Transparency
Digital platforms provide real-time data on transactions, making it easier for governments to monitor and enforce tax laws.
Withholding Tax Mechanisms
Platforms can withhold a portion of earnings as tax before paying workers, ensuring revenue collection.
One of the best examples of solutions in this category that truly work is traceCORE Platform Employment Tax Solution. It ensures gig workers contribute fairly to public finances, reduces the administrative burden on workers who may not be familiar with tax procedures, and creates a level playing field between gig workers and traditional employees.
The solution seamlessly integrates with government agencies for automated data exchange, ensures accurate calculation of taxes for the self-employed and IPs in compliance with legislation, creates electronic invoices in accordance with the legislation requirements, and quickly connects to any platform via API.

After the implementation, governments can expect increased tax revenue through automated tax collection from the self-employed and IEs and enhanced transparency in the digital services market.
Conclusion
Informal employment, while a necessary lifeline for billions, perpetuates poverty, exclusion from rights, and lost state revenues. Yet digital transformation offers a robust pathway to formalizing these workers — creating inclusive, resilient, and equitable economies.
Formalizing the informal economy using digital tax tools helps governments increase revenues to fund social programs, improves working conditions and social security for millions of vulnerable workers, and fosters innovation, investment, and sustainable economic growth.