Track and Trace for Governments
Differences in Product Marking Code Application Methods

In today’s fast-paced manufacturing and supply chain environments, product authentication and traceability have become essential for efficiency, compliance, and consumer safety. According to a 2025 study by the OECD and EUIPO, counterfeit products were valued at approximately $467 billion in 2021, representing about 2.3% of total global imports. That alone is extremely concerning.
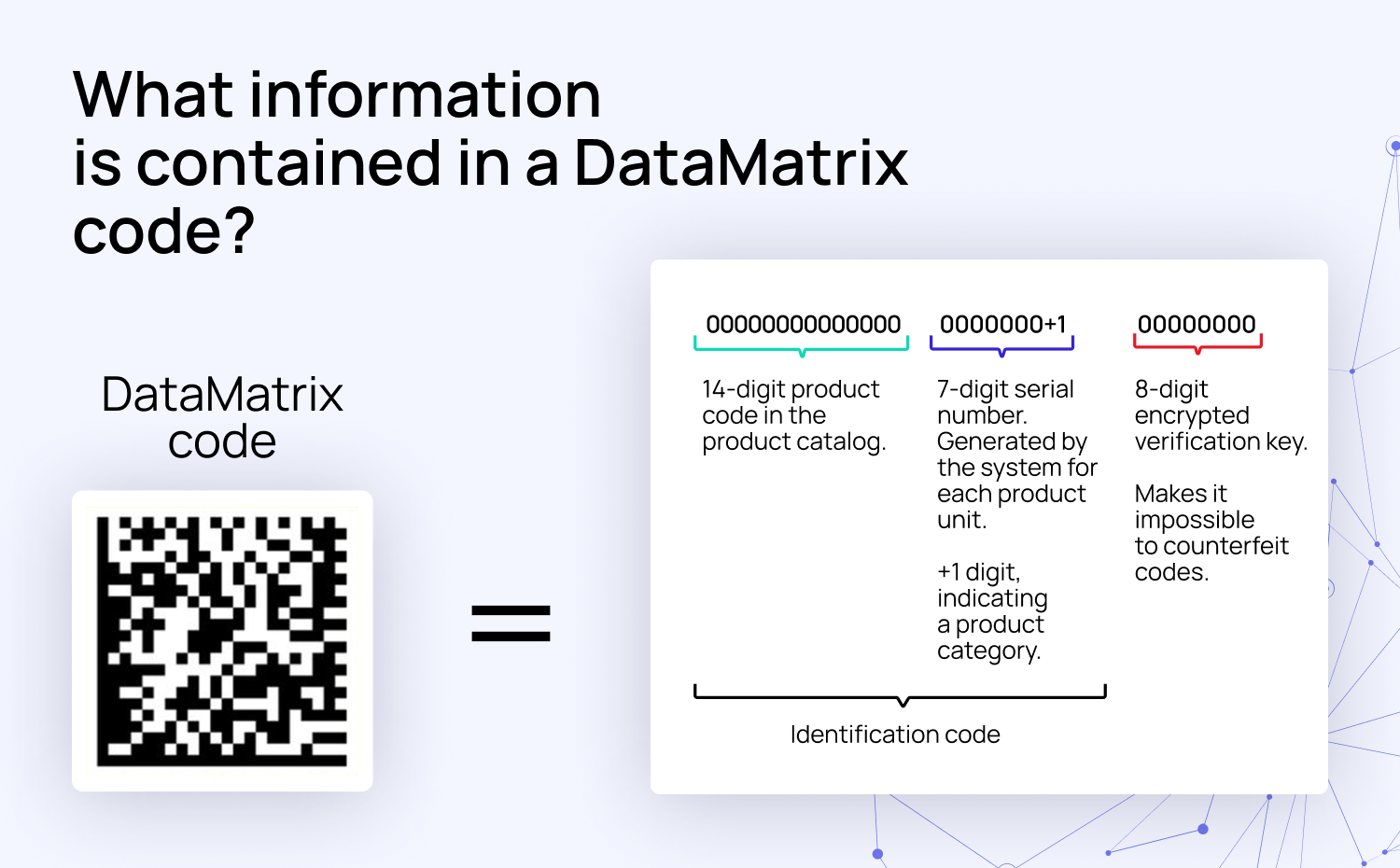
One of the most effective tools for product authentication across the supply chain is the DataMatrix code — a compact 2D code that stores large amounts of information in a small space.
But how are these codes actually applied to products? Is there just one universal way to do it, or companies have multiple options? Spoiler: there are several ways.
Let’s break it down.
How Do Product Marking Codes Help Authenticate Products?
While we have just established what DataMatrix codes are, but how do they actually help identify products?
Each DataMatrix code can store information that distinguishes one product from another — even if they’re the same model or batch. This unique ID links to a secure database containing various details, such as manufacturing date, origin, batch number, and destination. When scanned, the code can be checked against this database to verify whether the product is genuine or counterfeit.
However, the real magic happens when the DataMatrix code integrates with a Digital Track and Trace system: the product’s journey — from production to distribution to retail — is recorded.
What Is Digital Track and Trace?
Digital Track and Trace is a system that allows all supply chain participants — manufacturers, importers, distributors, and retailers — to monitor, record, and verify the movement of products throughout the entire supply chain from production to the end consumer.
Each scan at different points updates the product’s “digital history.” In case a product shows up in an unexpected location or time, the system flags it as suspicious or counterfeit.
This creates end-to-end transparency, making it nearly impossible for counterfeit goods to enter the legitimate supply chain undetected.

Digital Track and Trace is often confused with Digital Tax Stamps, which makes people use these two terms interchangeably. However, there is a difference, and we talked about it extensively in our “Digital Tax Stamps and Track and Trace: Is There a Difference?” post, so make sure to check it out.
What Else Makes DataMatrix Codes Vital for Businesses?
Unlike simple printed text or 1D barcodes, DataMatrix codes are compact, hard to replicate, and can include encrypted or encoded data. Advanced systems can even use cryptographic signatures — digital seals that verify the authenticity of the data itself.
Moreover, any alteration to the code (e.g., reprinting, tampering, or cloning) makes it invalid when scanned.
Consumers are also not powerless when it comes to spotting fake goods. Nowadays, they can scan DataMatrix codes using their smartphones. The scan connects to a secure database and confirms whether the product is authentic.
If you’re looking for a powerful Track and Trace system to tackle illicit trade in your country and protect brands from counterfeiting, we’ve got you covered.
traceCORE Digital Track and Trace will help you foster fair market competition and protect citizens from harmful products. Click here to learn more.
How Are Marking Codes Applied to Products?
There are actually several marking code application techniques available, each with its own benefits, limitations, and ideal use cases.
Further, we’ll explore the three main methods — laser marking, inkjet printing, and sticker labeling — and see how they fit into a Digital Track and Trace system.

1. Laser Marking Equipment
Laser marking uses a focused beam of light to etch or engrave the DataMatrix code directly onto a product’s surface. It’s a non-contact and permanent marking method widely used in larger-scale industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, automotive, metal manufacturing, etc.
.png)
Pros
-
Exceptional speed: Allows applying up to 30 codes per second, ensuring high marking quality and reducing the number of errors to a minimum.
-
Durability: Marks are permanent, resistant to wear, heat, and chemicals.
-
High precision: Ideal for small codes on delicate or complex surfaces, helps avoid code damage.
-
No consumables: No ink or labels are required, reducing long-term costs.
-
Clean and eco-friendly: No solvents or waste materials.
-
Low-maintenance: With service life up to 100 000 hours, very little maintenance is required.
.png)
Cons
-
Higher initial cost: Laser systems are costly to purchase and set up.
-
Limited on some materials: Depending on the equipment type, sometimes it doesn’t work well on transparent or reflective surfaces.
-
Safety requirements: Requires protective measures and training.
Best used for: High-volume, high-value manufacturing lines where permanence and quality are critical — e.g., medical devices, automotive parts, and electronics.
2. Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printing applies DataMatrix codes using high-speed nozzles that deposit ink directly onto the product surface. This method is flexible and cost-effective, suitable for printing on various materials such as paper, plastic, metal, or glass.
Inkjet DataMatrix printers are less expensive than the laser ones, yet still efficient enough to fit small- and medium-sized businesses.
.png)
Pros
-
Fast and flexible: Easily integrated into existing production lines.
-
Low initial investment: Affordable compared to laser marking, includes advanced coding technologies that meet most manufacturers’ needs.
-
Good for varied materials: Works on curved or irregular surfaces.
.png)
Cons
-
Maintenance required: Printheads can clog; ink supply must be monitored.
-
Less durable: Marks can fade, smear, or be removed by moisture or abrasion.
-
Consumable costs: Ongoing expenses for ink and solvents.
Best used for: Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) — affordable everyday products that are sold quickly, food and beverage packaging, and pharmaceuticals, where speed and versatility outweigh permanence.
3. Sticker Printers
Sticker printers print DataMatrix codes onto adhesive labels that are then applied to products or packaging.
Stickers can either be applied directly to individual products as part of the serialization process, or used during aggregation — where they’re attached to boxes, cartons, or pallets to link multiple serialized items into a single parent unit.
This method is flexible, low-budget and easy to implement.
.png)
Pros
-
Simplicity: Easy to use and replace.
-
High print quality: Clear, readable codes with detailed graphics.
-
Suitable for many materials: Can be applied to surfaces where direct marking isn’t possible.
.png)
Cons
-
Not permanent: Labels can peel, fade, or be damaged.
-
Higher consumable costs: Requires label rolls, ribbons, and adhesives.
-
Slower process: Label application can limit throughput, which is why this method isn’t the best fit for medium and large-sized businesses.
Best used for: Micro and small businesses, as it the least costly option available.
Conclusion
Selecting the right product marking method is essential to ensuring reliable data capture and smooth integration into your Digital Track and Trace system. Laser marking offers permanence and precision; inkjet printing provides flexibility and speed; while sticker labels deliver simplicity and adaptability.
By understanding the pros and cons of each approach, businesses can implement a marking solution that fits their production volume, product material, budget, and regulatory requirements.
After all, the main goal of the marking equipment is to enhance traceability, compliance, and operational efficiency — ensuring every product tells its story, from factory floor to consumer hands.
Related Posts
All postsDigital Tax Stamps and Track and Trace: Is There a Difference?
Digital Tax Stamps and Track and Trace systems are both used to fight illicit trade, but they work in fundamentally different ways. Only one provides real-time transparency and protection against counterfeiting. Read this post to learn more.


.webp)
