Track and Trace for Governments
What is Track and Trace for Governments: Technology Explained
.jpg)
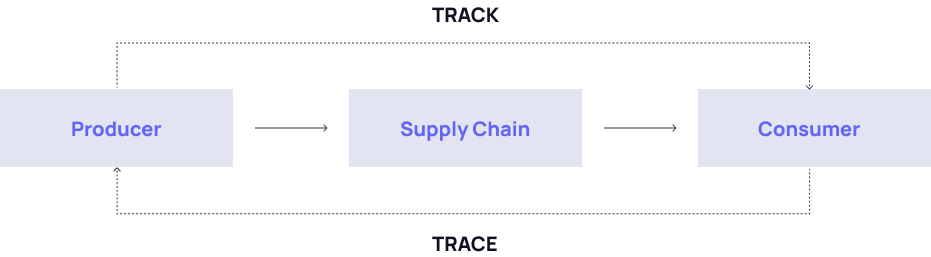
What Is Track and Trace?
Track and Trace technology is a versatile system to monitor the movement of products as they progress through various stages of the supply chain. It can be used for quality control and brand protection, which makes it a valuable tool for brand owners, manufacturers, and government entities.
Track and Trace helps curb the underground market, boosts tax revenue, safeguards brands against counterfeits, and shields consumers from substandard products. Yet, when mishandled, its application poses challenges for both government and business.
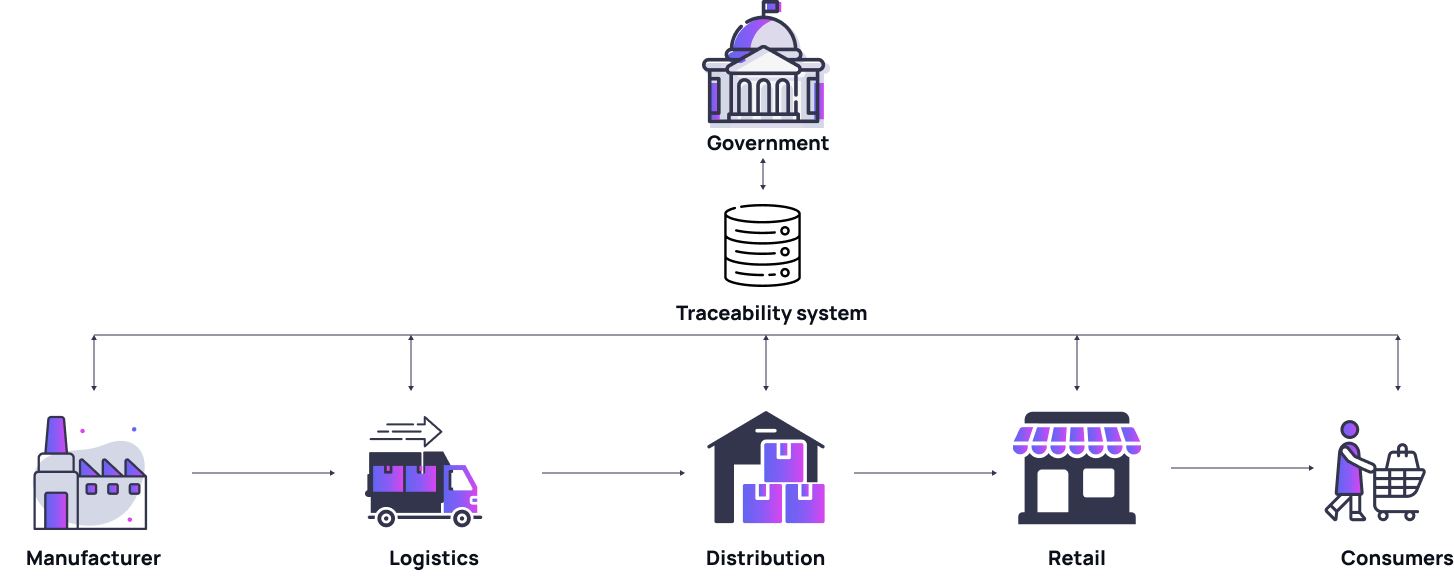
This technology can be broken down into two modules:
- Tracking involves the continuous monitoring of a product’s journey from its origin through different points in the supply chain.
- Tracing focuses on identifying the product’s exact place of origin. Essentially, it is pinpointing where it was manufactured.
.png)
The implementation of Track and Trace systems typically includes adding secure and unique markings to products.
These markings convey essential information — the product’s manufacturer, its place of origin, target market, the verification of tax payments, production and expiry dates, quality certificates, and any other relevant information.
Each product is assigned a unique and protected identifier, similar to a serial number.
Additionally, there are robust security features integrated to deter counterfeiting, which makes it extremely challenging to replicate or forge these markings.
The primary goal of Track and Trace technology is to ensure the authenticity of both the product and its associated identifier.
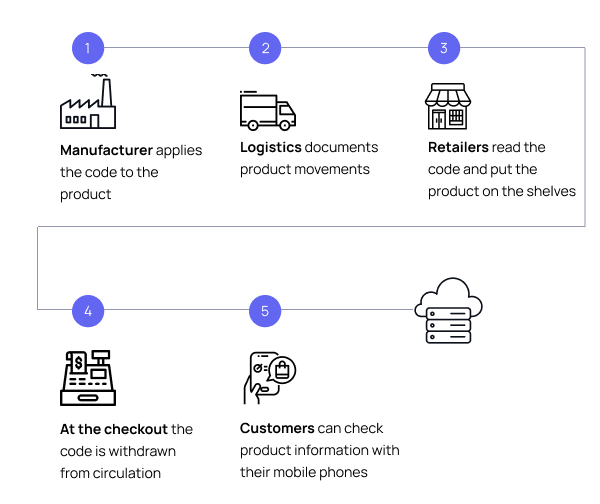
How Does Track and Trace Work?
- Manufacturers and importers kickstart the traceability process by registering on the national platform, detailing their products, and requesting unique codes.
- These codes become a product’s legal identity called ‘product passports’, and any item lacking them is deemed unauthorised.
- The codes, once applied, undergo activation on the production line through a camera, and this activation event is swiftly reported to the central system.
- As products journey through the supply chain, their every move is recorded and relayed to the central system, which creates a comprehensive trail.
Track and Trace implementation can happen at two levels: the company level and the state level.
At the company level, traceability solutions are often initiated by well-established brands in FCMG, pharmaceuticals, tobacco and beer industry. The main goal here is to protect products from counterfeiting and build customer trust and loyalty.
However, the most profound effect can be achieved when traceability implementation is driven by the government. In this scenario, the state mandates all market participants to adopt product labelling. This legal requirement extends beyond a specific manufacturer or product. It encompasses all products in the market.
Products lacking the code are deemed illegal. Any attempts to sell illicit goods are reported to the centralized system and immediate action can be taken. This approach proves highly effective in curbing the gray market, with experts estimating reductions of up to 5%.
.png)
Track and Trace for Governments Is a Win-Win for All Stakeholders
Implementing a robust Track and Trace system is a strategic move that benefits governments, manufacturers, and consumers. From one perspective, this comprehensive approach secures government revenues. From another, it also promotes fairness, transparency, and efficiency in the market.
All stakeholders stand to gain when the governments adopt Track and Trace. Technology benefits are detailed below:

- The system deters counterfeiting and ensures tax collections remain robust and reliable.
- Facilitates precise accounting for excisable goods, whether domestically produced or imported.
- Streamlines enforcement efforts by focusing on potential violators.
- Eases bureaucratic processes.
- Allows for swift responses to market fluctuations and emerging trends
- Enables the accurate prediction of potential shortages.
.svg)
- Improves brand protection and customer loyalty.
- Reduces administrative burden.
- Facilitates data-driven decision-making to optimize production, logistics, marketing and other operations.
- Easier product recalls lead to reduced legal and reputational risks.

- Utilizes mobile technology to authenticate tax stamps, which guarantees consumers genuine products.
- Enables direct communication, where consumers can verify product authenticity.
How to Make a Project Successful
Advanced Technology
First and foremost, the choice of technology is critical. Opting for modern, cutting-edge technology over older systems can significantly impact the efficiency and adaptability of your Track and Trace solution.
Direct Marking
Direct marking, which allows for the direct application of unique identifiers or codes to products, is another aspect. It reduces a manufacturer’s costs by minimizing the time and effort needed to apply the code.
Integration
You also need an adaptable Track and Trace system that seamlessly collaborates with your existing infrastructure, such as the Core Tax System, and boosts efficiency and data consistency throughout the supply chain. This ultimately allows for a smooth flow of information. traceCORE works according to that principle.
Architecture
Furthermore, the system’s architectural design plays a principal role in performance and scalability. A well-structured architecture enables your Track and Trace system to handle increasing workloads and add new product categories seamlessly.
Localization
Make sure that technology and the know-how stays within your country. The vendor must ensure that the local team is trained to continue to support the system.
Better Impact Through Holistic Implementation
The solution doesn’t solely lie in technology. What truly matters is the purpose and method of implementation. Take the extensive and multifaceted nature of labelling, applicable in both corporate and government areas. For Track and Trace to be truly effective, it must seamlessly connect with critical systems, such as the central tax service and electronic document management. In addition to ensuring product traceability, this integration extends its impact to a range of useful functions for those involved in trade turnover.
Equally vital is the economic viability of the technology. It should not only be modern and efficient but also economically feasible, which implies that the investment will align with its benefits. Unfortunately, this aspect is frequently overlooked and leads to instances where expected advantages fall short.
The choice of the supplier is paramount. Their proficiency ensures that the technology meets and perhaps even exceeds expectations, and this will result in high profits for participants, consumer protection, and streamlined business processes. Ultimately, success hinges on strategic choices that extend beyond technology adoption to unleash the full potential of labelling initiatives.
Future Horizons
Looking ahead, as Track and Trace technology progresses, governmental institutions and companies will use the data they collect to gain better insights into their supply chains. This will help them quickly spot problems and make improvements, which will lead them to greater efficiency and cost savings. The future holds a more secure and adaptable supply chain so that interested parties can thrive in changing markets.


.webp)
.jpg)