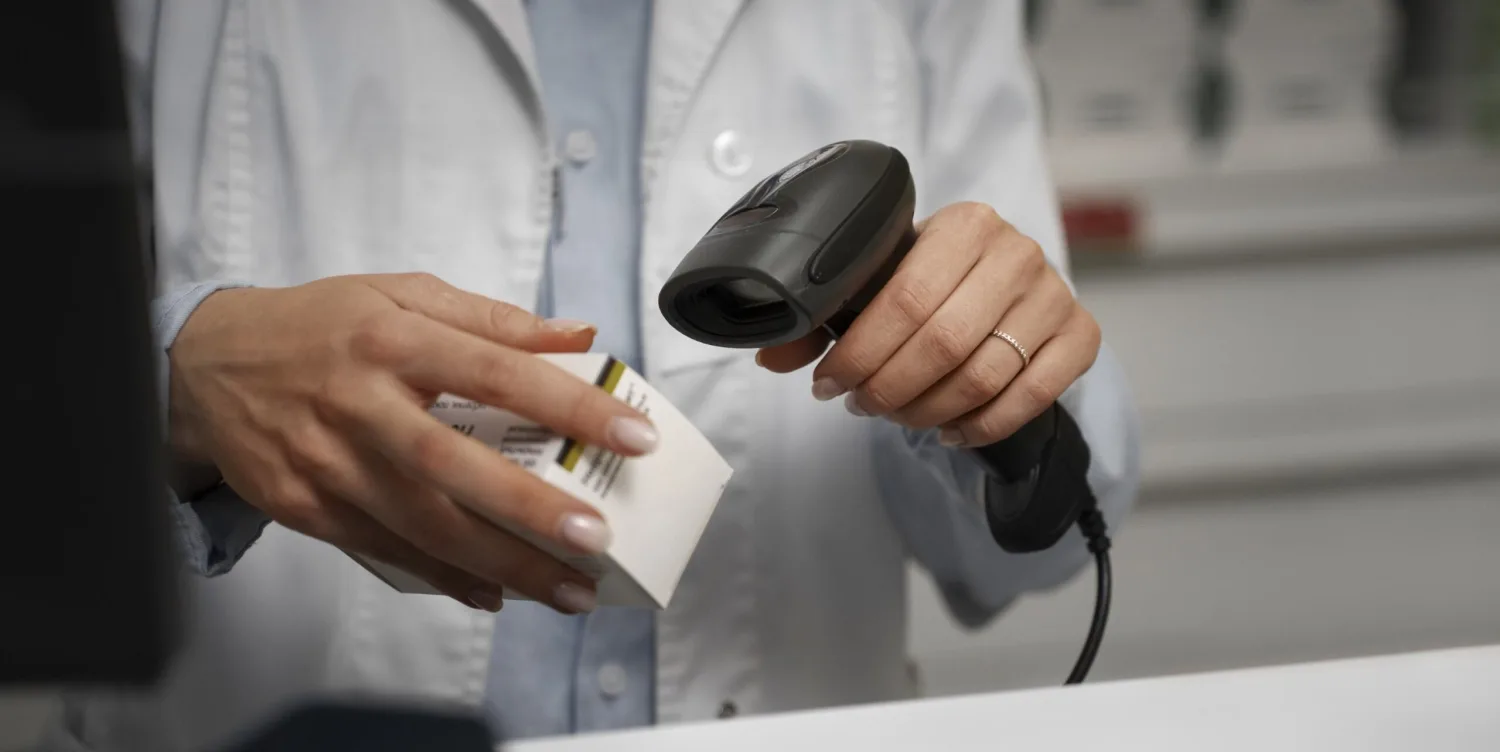

What Is a Tax Stamp?
A tax stamp is a small security label or sticker that’s put on products, either on the packaging or printed on them directly. It is typically used for FCMG products or items like cigarettes or alcohol to show that the required taxes have been paid to the government by the producer or importer.
Essentially, it’s a way of proving that the product is legal and has met the necessary tax obligations.
Tax stamps also serve other purposes. For one, their presence on a product gives consumers confidence that it’s genuine and hasn’t been tampered with. Additionally, when a tax stamp is placed over the opening of a product, it acts as a seal to prevent tampering or reusing the container.
And as you move into a more advanced digital sphere, these labels are starting to include special codes that help monitor the production process and track products as they move through the supply chain. This means they’re also helping ensure product authenticity and traceability.
The technology is new, so it is not inherent to traditional paper stamps. But it is becoming a more necessary measure for those who want to ensure product authenticity and traceability.
The Problem with Traditional Tax Stamps
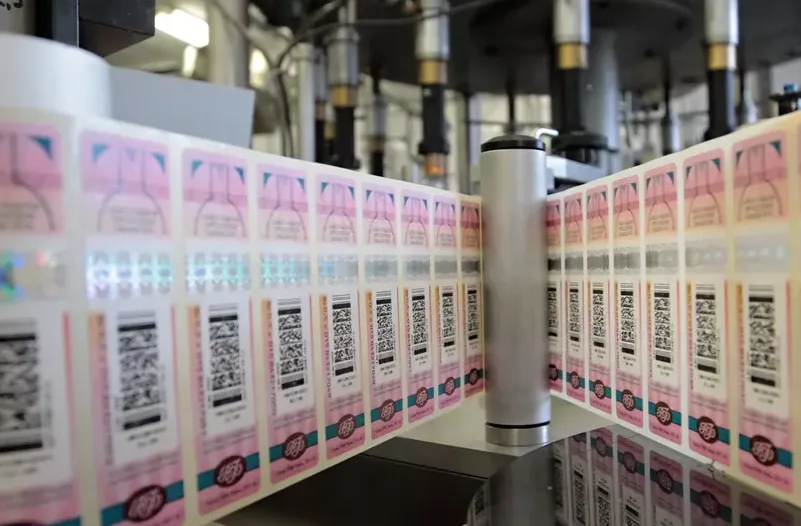

Traditional tax stamps aren’t sufficient with their security features to combat modern counterfeiting effectively. Yet, paper stamps have significant security measures. But compared to digital stamps, which use advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms, they’re more prone to putting collection and product authenticity at risk.
Buying tax stamps in large quantities is a common practice that saves money for the state, but it can backfire if the state can’t use all of them due to counterfeiting. Criminals may quickly copy them, which results in financial losses for the state.
Plus, when counterfeit methods are discovered, it’s challenging to rectify the issue because the same stamps are still in circulation. This, in turn, prolongs the risk of counterfeiting.

Another crucial point is that traditional tax stamps provide minimal insight into the movement of products. Without traceability options, manufacturers and regulatory authorities can’t effectively track the journey of goods from the point of manufacture to the end consumer.
Finally, traditional tax stamps primarily serve as regulatory compliance tools without offering tangible benefits to manufacturers. They end up costing manufacturers more money to buy, apply, and keep. Since these stamps don’t improve security and traceability or protect the brand, manufacturers see them as expensive hassles rather than useful tools for supply chain integrity.
There’s a need for globally aligned solutions that benefit everyone involved. Governments must understand the benefits of securing supply chains with track and trace solutions. Similarly, everyone in the supply chain who interacts with government agencies should know what the technology can do for them.
What Are Digital Tax Stamps, and How Do They Work?
Digital tax stamps (DTS) are special labels that are stuck or printed directly on the packaging of excisable goods. DTS serve a similar purpose to traditional stamps by confirming that the products are genuine in addition to being taxed correctly.
They similarly include security and tamper-proof features but go further by offering track and trace capabilities through embedded codes that can be read using software.

Tax authorities are already starting to introduce electronic tax stamps to replace paper ones. In various tax authorities around the world, electronic tax stamp systems have been implemented with better security features made to enable production tracking. Old-fashioned tax stamps are also used for that purpose, but they don't have a traceability option.
Anyone involved in the supply chain of goods subject to the new system must check and confirm the authenticity of both the electronic tax stamps and the goods themselves before accepting them into their premises or handling them in any way.
How Do They Compare to Traditional Tax Stamps? Do They Work?
Traditional technologies
- Rely on outdated, proprietary methods reminiscent of 19th-century technology.
- Lack of interoperability and collaborative features.
- Involve direct marking with special ink that may not be readable by all stakeholders.
- Are characterised by a lack of transparency, efficiency, and compatibility, which manufacturers aren’t happy about.
- Are associated with high costs and limited effectiveness in addressing modern supply chain challenges.
Modern solutions
- Include digital codes, adhering to open standards, such as GS1.
- Able to directly mark products for readability by all stakeholders using standard smartphones.
- Designed to meet manufacturer requirements for operational efficiency and interoperability.
- Compatible with various systems including B2B, B2C, and electronic cash registers (ECR).
- Compliant with regulations, including the FCTC for tobacco control.
- Effective in combating illicit trade and tax evasion through collaborative efforts among stakeholders.
The Benefits of Using Digital Tax Stamps
Enhanced Traceability
Digital stamps provide a clear audit trail, allowing for tracking of the product's journey from production to distribution. This improves transparency and helps in identifying issues or verifying product authenticity.
High-level security
Digital stamps are secure, unique, and embedded into the product. They are irremovable and non-reusable because they’re stored electronically on a secure server.
Detailed information
Digital tax stamping allows for reporting detailed information about the product, such as the brand and variant.
Innovative solution
Digital technologies can evolve into comprehensive solutions like tracking and tracing if required by authorities.
Implementation and Adoption
The introduction of digital tax stamps consists of roughly three main phases: inception, implementation, and reporting.
In the inception phase, the goal is to set clear objectives and plans by aligning the teams involved. This involves meeting with the implementation team, identifying stakeholders, refining the project approach, and submitting an inception report.
During the implementation phase, the focus is on gathering data to evaluate the impact of stamps on a given industry. Some of the steps include assessing the effect on government revenue and business costs, comparing prices, and exploring available solutions.
In the reporting phase, the project team presents findings and recommendations, documents lessons learned, and ensures all requirements are met. This is done by preparing a final report, hosting a feedback event, and confirming deliverables. When introducing a new system for the first time, there may be challenges as taxpayers get used to it. However, these challenges can be overcome as they gradually adapt to the new way of doing things.

Conclusion
Digital technology presents a more effective and secure alternative to traditional tax stamps. Paper stamps can be copied, counterfeited, and reused since they are only affixed to product packaging, whereas digital codes are irremovable and unique. These codes are stored electronically on a secure server, which maximizes authenticity and traceability.
traceCORE Digital Track and Trace makes the administration of unique marking codes simpler for both authorities and manufacturers. Operations are paperless, conducted online, and eliminate the need for processes involving wasted costs.
It is specifically the Digital Track and Trace technology that enables real-time tracking of product movement through the supply chain.
If you want to learn more about the difference between Track and Trace and Digital Tax Stamps, check out this post.


.webp)
.webp)