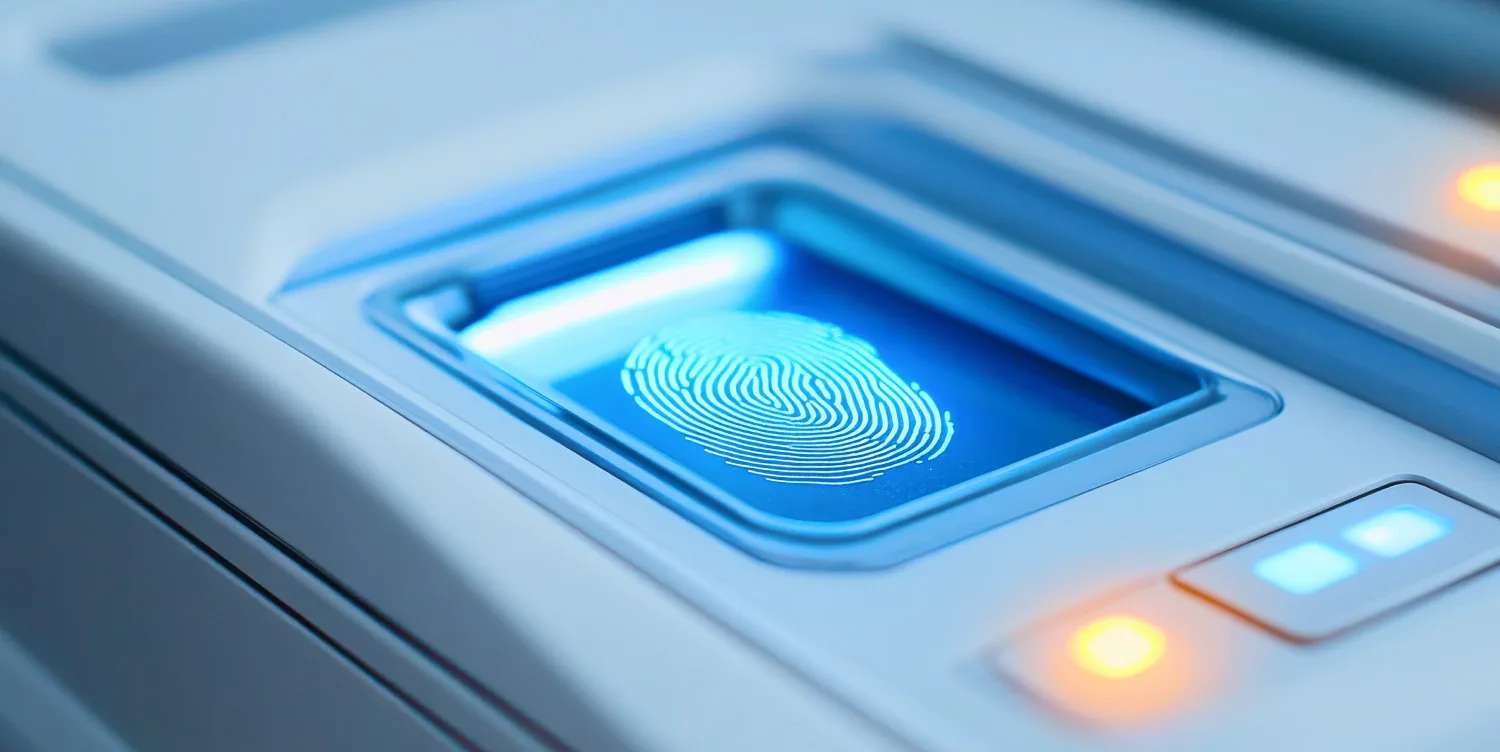

Biometrics has long stopped being just a fancy word in the tech world. Over the past decade, this technology has emerged as a central focus and a vital tool for numerous government and enterprise initiatives.
In this post, we will explore what makes biometric technology indispensable when it comes to improving national security: safeguarding data, granting access to authorized users, securing and issuing national documents to their rightful holders, and beyond. You will also learn more about traceCORE National Biometric System, and how governments around the world can benefit from implementing this solution.
What Is Biometrics?
Biometrics refers to a collection of technologies and methods designed to recognize, authenticate, and identify individuals based on specific physical or behavioral traits.
According to ITU, those traits must be:
-
Universal: Every person should have the biometric trait.
-
Unique: No two individuals should have the same trait.
-
Permanent: The biometric trait should remain consistent throughout a person's lifetime.
-
Collectable: The biometric trait should be measurable in quantitative terms.
Biometric technologies are crucial in identity management programs today because they offer rapid and precise methods for authentication and identification. The use of biometric data provides a strong defense against unauthorized access and fraud that occurs during data breaches and identity theft incidents.
Most Common Types of Biometric Authentication
Fingerprint Scanners
Fingerprints are distinct to every person and have been employed for identification for more than a century. This method involves recording the patterns and ridges on a person's fingertips to generate a one-of-a-kind biometric template.
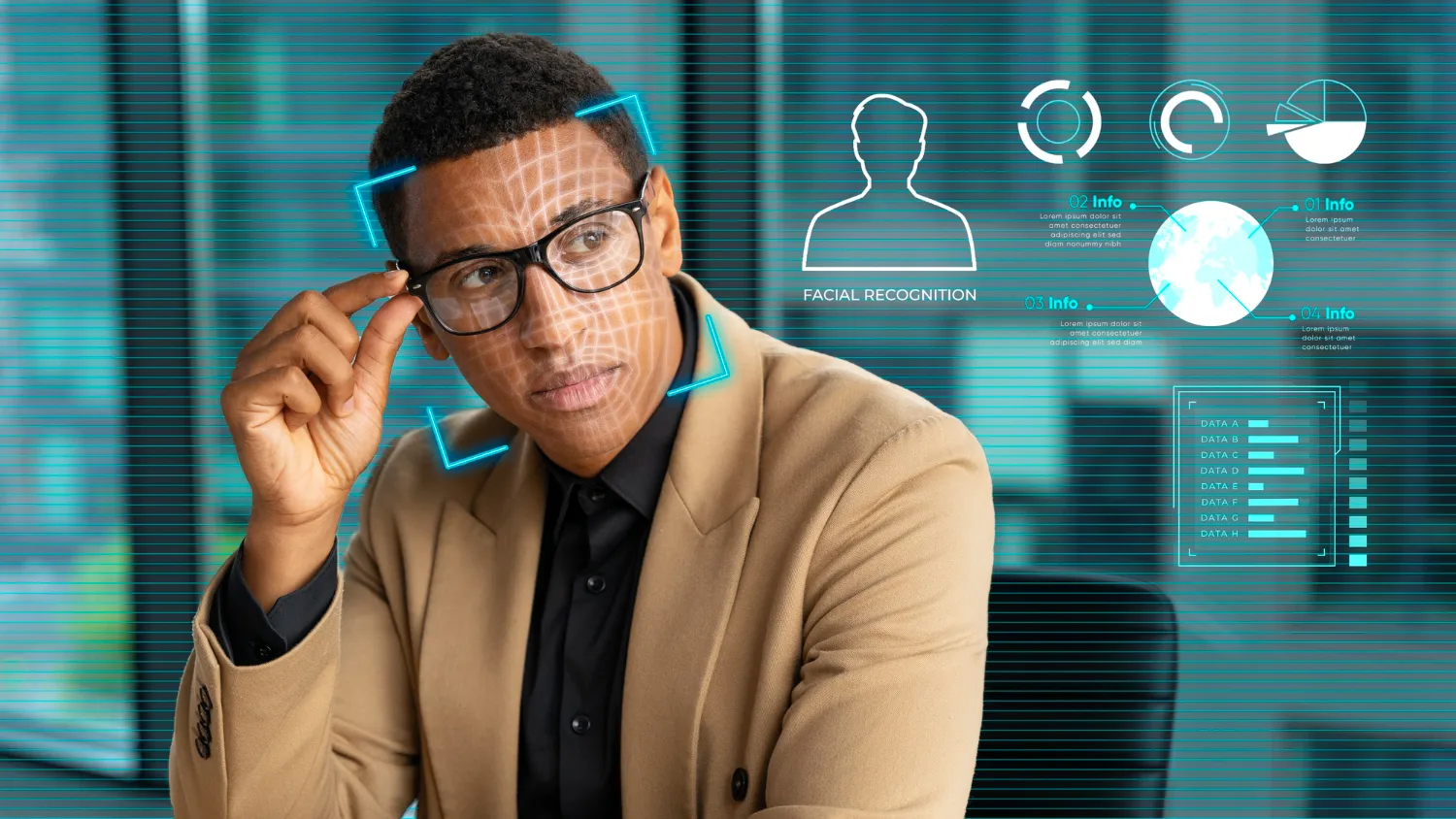
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition examines a person's facial characteristics to confirm their identity. The system captures and evaluates different facial features, including the distance between the eyes, the shape of the nose, and the contours of the face.

Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology can authenticate a person’s identity by examining their vocal traits, such as pitch, tone, and pronunciation. It captures distinct voice patterns and compares them to pre-existing templates for verification.

Eye Scanners
Eye scanners encompass both retina and iris scanners.
Retina scanners emit a bright light onto the eye to highlight blood vessel patterns, which are then read and compared to data stored in a database.
Iris scanners analyze the unique patterns in the colored ring around the pupil.
Eye scanners are great for hands-free identification, though they can be less reliable if the person wears glasses or contact lenses.
Biometric Authentication and Its Types
Biometric authentication is a security method that verifies a user's biometric features when attempting to access a device or system. The access is granted only if the provided parameters match those stored in the database for that specific user.
Biometrics Institute determines numerous types of biometric authentication, but we are going to explore four of the most common ones in detail.
What Can Be Considered Biometric Data?
Biometric data consists of three primary types of identifiers:
Morphological
These are physical features, including the shape of your face, fingerprints, or the structure of your eyes (retinas or irises).
Biological
This type involves physical samples from your body, such as blood, DNA, or other bodily fluids.
Behavioral
This includes unique behavioral traits, like keystroke patterns, signatures, handwriting, or walking style (gait).
Wondering how your country can benefit from implementing various digital transformation tools?
Contact us today to learn how our products can help countries improve tax compliance and generate more revenue.
How Does Biometric Authentication Work?
The way biometric authentication works is actually pretty simple: it identifies an individual by comparing their biometric data with information stored in a database. If the data matches, access is granted. Various types of biometric scanners are used, such as fingerprint, facial recognition, iris, and hand vein scanners.
This is how it works:
Capture
A reader or scanning device collects the biometric data for authentication. For instance, a facial recognition scanner records facial features.
Conversion
The system transforms the captured biometric data into a digital format.
Storage
The data is then stored either in a central database or on the device, where it can be used for comparison with later live inputs.
Authentication
A live sample is taken and compared against the stored digital data. For example, when a person’s face gets scanned, the new sample is matched with the stored record. If there’s a match, authentication is confirmed.

Industries that Use Biometric Data
Biometric data is used to confirm the identity of employees, customers, and users in a wide range of industries.
These are some of the industries that often use biometric data:
Role of Biometrics in National Security
Biometrics has become a crucial element in national security, playing a key role in border control, law enforcement, and counter-terrorism efforts. This technology offers the potential for major advancements and changes in the ways countries safeguard their citizens.
Biometric systems provide quick and precise identification capabilities. For example, facial recognition technology can quickly scan and match thousands of faces to a database of known individuals. Likewise, fingerprint scanners have become more accurate, allowing for fast identification of suspects at crime scenes.

The power of biometric technologies lies in their ability to resist being forged or replicated. Traditional forms of identification that can be stolen or duplicated. However, biometric data is unique to each individual, making it hard for criminals or terrorists to impersonate others.
Progress in biometrics is expected to further improve its effectiveness. Brand-new technologies, such as gait recognition (identification by walking patterns), and ear recognition (analyzing the unique shape of a person's ear), are being tested nowadays. These innovations have the potential to offer even more precise and dependable identification methods.
6 key ways how governments worldwide can benefit from implementing biometric systems
Enhanced Accuracy and Identity Verification
The increased precision in verifying identities is definitely one of the key advantages of biometrics in national security. To confirm people’s identities, biometric systems use different methods, like fingerprint, facial, and voice recognition, as well as other modalities.
By matching biometric data with existing databases, security personnel can reliably verify an individual’s identity, minimizing the chances of impostors or people using fake documents. By doing so, it’s possible to enhance overall security by ensuring that only authorized individuals are allowed entry into restricted areas.
Better Border Security and Immigration Control
Biometrics are essential in enhancing border security and immigration enforcement. Authorities can confirm the identity of travelers by collecting biometric data, like fingerprints or facial images. This allows for the detection of individuals with fraudulent identities, identifying those with criminal records, and preventing unauthorized individuals from entering the country. Biometric screening systems allow the authorities to add a strong security layer at border checkpoints, protecting national borders and supporting effective immigration control.
Preventive Threat Identification and Mitigation
Biometric screening systems play a key role in the proactive detection and prevention of threats. In places like airports, security personnel can detect potential threats in real-time by cross-referencing individuals' biometric data with watchlists or databases of known criminals or people with immigration violations. This strategy enables authorities to act swiftly, stopping suspicious individuals from boarding flights or accessing restricted areas.
More Efficient Forensic Investigations
Biometric systems also aid in forensic investigations, as the biometric data collected during the screening process can help detect individuals who engage in criminal activities or undergo ongoing investigations. This allows the authorities to link suspects to crimes and identify potential threats in a timely manner.
Strengthened Counter-Terrorism Efforts
Biometric systems play a crucial role in enhancing counter-terrorism efforts by identifying and tracking individuals who may pose a threat to national security. By comparing biometric data (such as fingerprints or facial recognition) across global databases, authorities can quickly flag potential terrorist suspects or those on watchlists. This helps prevent their movement across borders and enables a more coordinated response in tackling terrorism. Biometrics ensure that individuals who attempt to disguise their identity or use false documents are caught, significantly contributing to the detection and prevention of terrorist activities.
Improved Efficiency and Faster Travel
Biometric systems at airports greatly enhance efficiency and accelerate travel processes. Passengers can go through a simplified identity verification process, removing the need for manual document checks. For instance, facial recognition technology is utilized at multiple stages, including check-in, security checkpoints, and boarding gates, enabling passengers to move through the process smoothly without the need to present physical documents multiple times. As a result, waiting times, congestion, and bottlenecks are reduced, which helps people have a much better travel experience.
What Is traceCORE National Biometric System?
traceCORE National Biometric System (NBS) is a government-operated digital platform designed for remote and in-person identity recognition and verification using a person’s physiological and biological characteristics.
It enhances security across various operations and services, while also improving user convenience. Managed by the government, the NBS sets its policies and standards.
Key areas of implementation include the public sector, financial sector, travel and immigration, healthcare, corporate use, and retail. The system strengthens security measures, streamlines processes, and supports accurate identity verification in these critical sectors.
Implementing the traceCORE National Biometric System (NBS) enables governments to expand access to services that require legally verified identities.
Benefits of Using traceCORE National Biometric System
Did you know that a whopping 80% of hacking-related breaches involve compromised and weak credentials? And not only that — hundreds of billions of dollars are lost annually due to fraud and improper payments.
Criminals armed with advanced technology have turned fraud into a profitable business, targeting governments, businesses, and individuals around the world, resulting in massive financial losses. Despite this growing threat, many governments have been hesitating to implement identity verification technologies that combat fraud, safeguard sensitive data, and protect citizens from unauthorized access.
Here are the benefits countries worldwide can experience from using traceCORE National Biometric System:
For Governments:
-
Enhanced public safety and better protection of citizens' personal data.
-
Decreased fraud through the implementation of a reliable identification system.
-
Greater accessibility to government and commercial services for citizens.
-
Improved service quality, leading to higher citizen trust.
For Businesses:
-
Reduced expenses through process automation and enhanced time tracking.
-
Enhanced labor protection and workplace safety systems.
-
Bolstered information security measures.
-
Reduced fraud and other illegal activities.
-
Established user-friendly and comfortable work environment for employees.
For Consumers:
-
Enhanced privacy protection for personal data.
-
Security measures during travel, work, and large events.
-
Easier access to government and commercial services.
-
Contactless technology for health and safety.
For more information about this solution, please visit the traceCORE National Biometric System page on our website.
Conclusion
By utilizing technologies like facial, fingerprint, voice, iris and retina recognition, biometrics improve the accuracy of identity verification, streamline travel processes, and play a key role in proactive threat detection and prevention. Biometric screening systems serve as a crucial asset in safeguarding national security.
The adoption of traceCORE National Biometric System offers significant advantages across multiple sectors, helping governments, businesses, and individuals combat the growing threat of fraud and data breaches. Using this solution, countries worldwide can better protect their citizens, reduce fraudulent activities, and promote a safer, more efficient digital landscape.

