Government Business Intelligence
How Big Data Analytics and Business Intelligence Can Help Tax Authorities
According to Straits Research, the global business intelligence (BI) market was valued at USD 30.1 billion in 2024. It is expected to expand from USD 36.82 billion in 2025 to USD 116.25 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.98% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
These changes occur due to the rise of emerging technologies, rapid advancements in automation and digitization, along with the latest innovations and developments, as well as collaborations and partnerships among key players in the country.
An analysis conducted by PwC showed that tax authorities can often have a hard time developing and implementing a cohesive technology strategy with long-term measurable objectives. Having a strategy like that can help transform the ever-growing data flow into actionable insights. In reality, tax administrations frequently turn to solutions with shorter-term effects instead of farsighted data-driven strategies.
Having a data-driven strategy enables tax authorities to make decisions that support both their own goals and their country's long-term socio-economic objectives.
It’s also critical for tax administrations to have the right tools to implement an effective strategy. In this post, we will discuss how Big Data analytics and business intelligence help tax authorities across the world, and why traceCORE Government Business Intelligence (BI) is a solution that can make a huge difference.
What Is Big Data and Business Intelligence (BI)?
Big Data
Big Data refers to extensive collections of varied data – including structured, unstructured, and semi-structured – that are produced rapidly and in large quantities. More and more businesses are leveraging this data to gain valuable insights and enhance their decision-making. However, traditional data storage and processing methods are insufficient to manage and analyze it effectively.
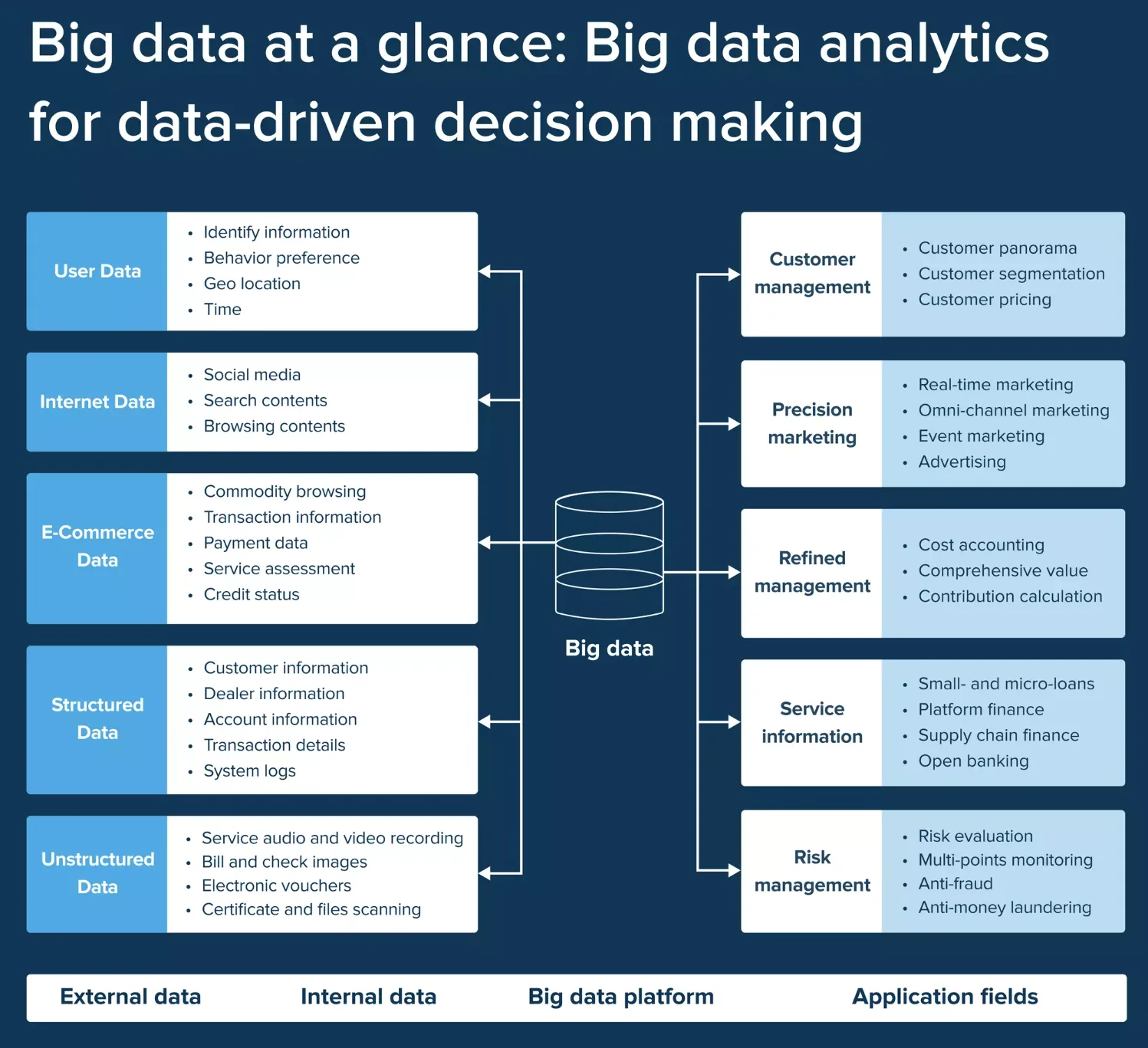
Key Big Data Characteristics
Business Intelligence (BI)
Fortune Business Insights defined business intelligence (BI) as a technical and procedural framework that collects, stores, and analyzes data generated by an organization’s operations. It includes process analysis, data mining, descriptive analysis, and performance benchmarking.
As organizations place greater emphasis on strategic decision-making, gaining valuable insights, enabling faster and more accurate reporting, and boosting productivity, the demand for these solutions continues to rise. Consequently, with the growing push for digital transformation, key players in the market are focusing on new advancements, innovations, and collaborations.
The market is primarily driven by the widespread use of e-commerce and the growing adoption of data-driven business models across small, medium, and large organizations.
The increasing demand for cloud-based business solutions in the SME (small and medium-sized enterprises) sector is fueling market growth. Growing awareness of the benefits offered by BI software presents significant opportunities for organizations to better target customers and improve user experience.
A key feature of BI software is its data scalability, with options like subscription, pay-per-use, and pay-as-you-go helping organizations scale their data efficiently. Additionally, BI software aids in tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) by utilizing a suite of tools that leverage big data to create valuable metrics for evaluating feedback.
According to Statista, the market size for business intelligence and analytics software applications is forecast to increase worldwide over the next few years from $15.3 billion in 2021 to more than $18 billion in 2026.

Source: Apps Run The World, & Statista. (September 23, 2022). Size of the business intelligence and analytics software application market worldwide, from 2019 to 2026 (in billion U.S. dollars) [Graph].
According to the BARC Score Enterprise BI & Analytics Platforms, Generative AI (GenAI) has significantly impacted the market due to its vast potential to simplify tasks for many software users. As a result, nearly every BI and analytics vendor is exploring how this rapidly developing trend can enhance their software and is developing their own GenAI strategies.
Contact us today to learn how you can transform tax authorities in your country and discover powerful AI tools that can be implemented by governments worldwide.
How Big Data and BI Can Assist Tax Authorities Worldwide: 8 Key Instances
Improved Fraud Detection
Big data analytics can identify unusual patterns and anomalies in financial transactions that could indicate fraudulent activity or tax evasion. Tax authorities can use BI tools to cross-check tax filings with third-party data, such as bank transactions, to spot inconsistencies and prevent fraud.
Enhanced Risk-Based Auditing
BI tools allow tax authorities to use predictive analytics to identify high-risk taxpayers and businesses for audits. By analyzing past behaviors, sector data, and economic indicators, they can target audits more effectively and ensure resources are allocated to the most critical cases.
Accurate Tax Revenue Forecasting
By examining historical data, economic trends, and patterns of taxpayer behavior, BI tools enable tax authorities to forecast tax revenues with greater precision. This helps governments plan budgets and fiscal policies effectively.
Automation of Routine Tax Collection
Automation through BI and big data reduces manual processing in tax collection. Tax authorities can automate routine tasks such as matching taxpayer data with third-party sources, reducing errors, and speeding up collection cycles.
Better Cross-Border Collaboration
In an increasingly globalized economy, big data analytics enable tax authorities across different countries to share information and collaborate in real-time. This is especially useful for combating international tax evasion, money laundering, and transfer pricing manipulation.
Personalized Taxpayer Services
Using data analytics, tax authorities can better understand taxpayer behavior and needs. This allows them to provide personalized services, such as tailored reminders, assistance, and advice, which helps improve compliance rates and taxpayer satisfaction.
Real-Time Compliance Monitoring
Big data allows tax authorities to track and monitor tax compliance in real-time. This helps them identify trends or emerging non-compliance issues, enabling quick interventions to ensure tax laws are adhered to.
Improved Taxpayer Education
Data analytics enables tax authorities to identify common areas of confusion or misunderstanding among taxpayers. By analyzing tax filings and interactions, tax authorities can develop targeted educational campaigns and resources to improve taxpayer knowledge and compliance.
What is traceCORE Government Business Intelligence (BI)?
traceCORE Government Business Intelligence (BI) is a digital platform designed to collect, manage, and analyze large volumes of data related to the country's B2B and B2C transactions, providing insights that help shape government strategies and operations.
traceCORE Government BI gathers and processes data from B2B and B2C E-Invoicing solutions, as well as the actionable insights generated through business analytics.
Government Business Intelligence can be utilized to answer questions about past events, make predictions, and forecast future outcomes.
Key Features

Financial Projections
Daily and monthly average revenue, profit margins, revenue forecasts, projected expenses, and long-term profitability outlook.

Operational Efficiency Metrics
Key performance indicators such as average supply chain performance, inventory turnover rates, and customer satisfaction scores.

Geospatial Analysis
Utilizing mapping tools to visually display market distribution, customer demographics, and infrastructure networks, offering investors valuable insights into geographic opportunities and potential challenges.

Market Size and Growth
The average annual growth rate of the target market, along with an estimate of the total market size.
How traceCORE Government BI Works
Big Data Sources
traceCORE Government BI integrates with B2B and B2C E-Invoicing solutions, the Tax Authority’s information systems, Fiscal Data Operators, and other big data sources.
Data Collection
Gathering and cleaning big data from multiple sources using automated extract, transform, and load (ETL) processes.
Analysis
Analyzing the data for trends or unexpected patterns using tools such as data mining, data discovery, and data modeling.
Visualization
Creating data visualizations, graphs, and dashboards to allow users to explore different levels of data.
Action Plan
Developing actionable insights by comparing historical data with key performance indicators (KPIs). These insights may lead to process improvements, policy changes, supply chain optimization, and more.
1.webp)
Benefits of Using traceCORE Government BI
For Governments
-
Boosted revenue through enhanced efficiency, reduced fraud and errors, and improved tax collection.
-
Enabled real-time monitoring of economic indicators across goods categories, industries, and regions.
-
Fostered innovative policymaking and improved service delivery.
-
Attracted investments and strengthened the private sector.
-
Enhanced productivity and performance of government authorities.
-
Increased citizens' economic awareness and engagement.
For Tax Authorities
-
Enhanced tax compliance through analytical and control efforts.
-
Detection and prediction of tax fraud using AI tools.
-
Rapid and thorough assessment of taxpayers' risk profiles.
-
Real-time, accurate, and detailed reporting by industry, region, inspectorate, and taxpayer.
-
Data-driven decision-making for tax policies and reforms.
For Businesses
-
Boosted business growth through an optimized marketing strategy driven by big data analytics.
-
Reduced administrative workload by minimizing inspections and automating tax payment processes.
-
Gained valuable insights into industry attractiveness, enabling more informed investment decisions.
-
Improved product development and increased customer satisfaction by predicting customer needs.
-
Enabled real-time KPI monitoring, with detailed tracking down to individual points of sale and receipt lines.
-
Streamlined resource management and enhanced operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The integration of big data analytics and business intelligence into tax systems offers immense potential for tax authorities to streamline their operations, improve compliance, and optimize revenue collection. These technologies provide actionable insights that empower governments to make informed decisions, detect fraud, and enhance transparency, ultimately leading to more effective and efficient tax administration worldwide. As the use of big data continues to evolve, tax authorities can better respond to changing economic conditions and the needs of their taxpayers.
By implementing traceCORE Government Business Intelligence (BI), governments worldwide gain significant advantage by driving efficiency, transparency, and growth across sectors.
